The year 2023 has witnessed one of the most brutal and intense phases of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict in recent history. Hamas terrorists have launched a relentless barrage of rockets into Israel while armed gunmen infiltrated Southern Israel. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu declared, “We are at war, and we will win it.” While reminiscent of previous clashes, this Israeli-Palestinian conflict is deeply entrenched in a complex history dating back to the First World War.
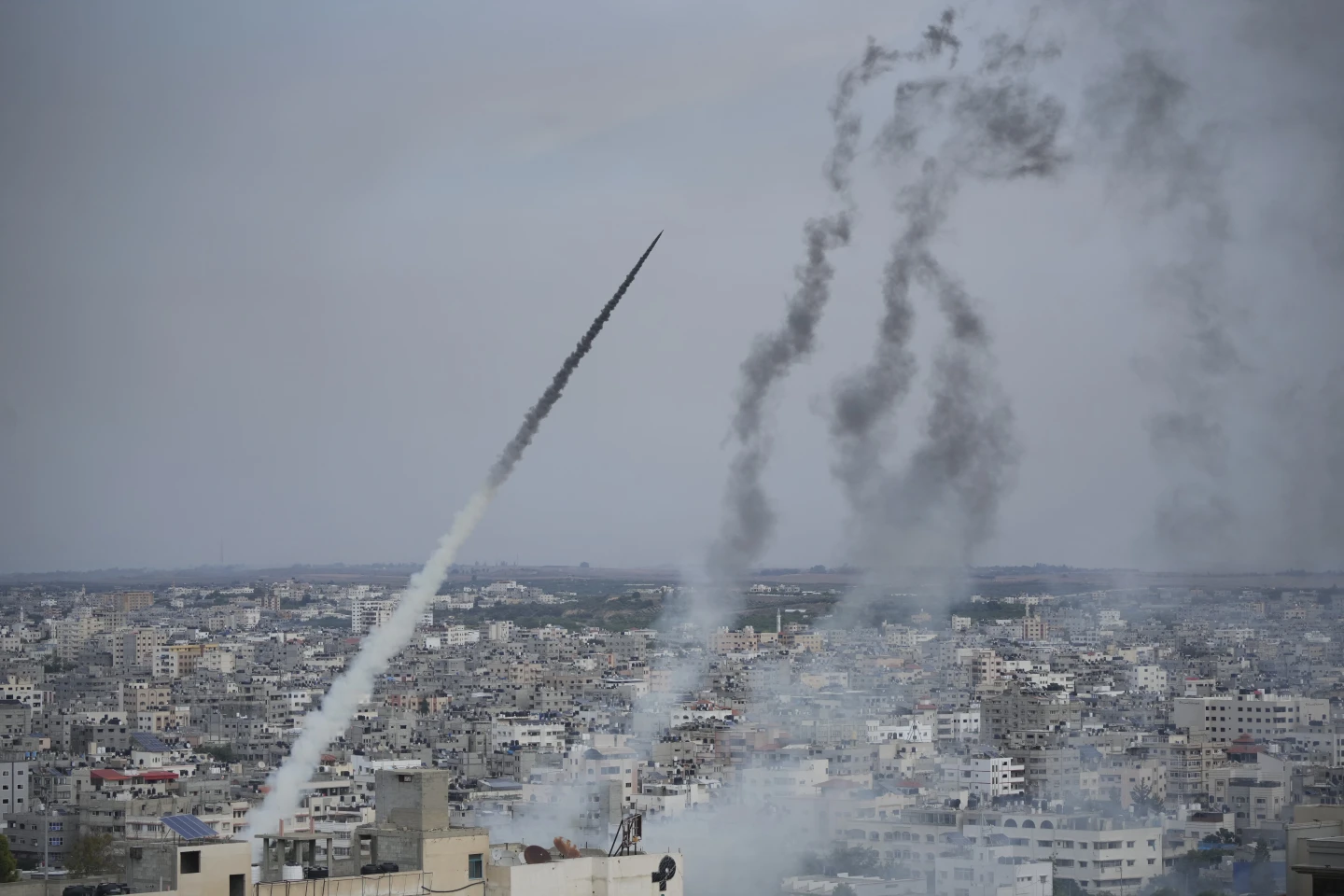

Hamas terrorists have launched a relentless barrage of rockets from Gaza City towards Israel on Oct. 7, 2023
Ancient Origins: Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Rooted in Antiquity
The origins of this Israeli-Palestinian conflict trace back to pre-biblical times when the Palestinian territories encompassed what we now know as Israel, Gaza, and the West Bank. Both Israeli Jews and Palestinian Arabs have deep historical, cultural, and identity ties to these lands and the ancient city of Jerusalem, which remains one of the most fiercely contested cities globally, according to The Associated Press.
Ottoman Rule and the British Mandate
The Ottoman Empire held sway over this region for approximately four centuries until its defeat, alongside Germany, in World War I. The League of Nations granted Britain control over Palestine in 1920 through the British Mandate. In 1917, the British government expressed support for establishing a Jewish state in Israel with the Balfour Declaration. While endorsing a Jewish state, this declaration also committed to protecting the civil and religious liberties of non-Jewish communities in Palestinian territories.
The Holocaust and Jewish Immigration
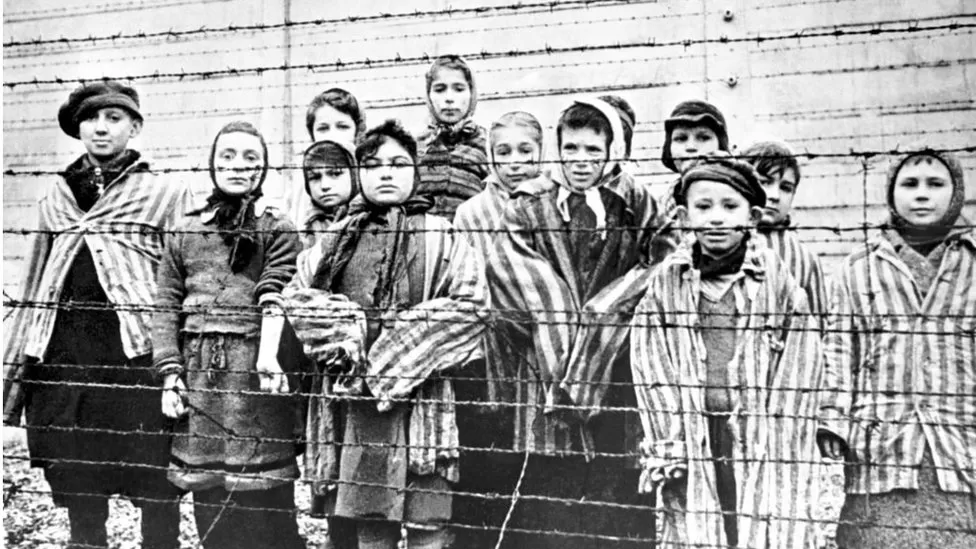

A group of child survivors behind a barbed wire fence at the Nazi concentration camp at Auschwitz
The period from 1922 to 1947 saw a significant influx of Jewish immigrants from Eastern and Central Europe, driven by persecution and the devastation of their communities during World War II and the interwar period. The Holocaust, which resulted in the murder of over 6 million European Jews, left many survivors stateless. However, as Jewish immigration surged, it displaced numerous Palestinians, triggering tensions and violence.
Early Clashes: Hebron Massacre and Palestinian Riots
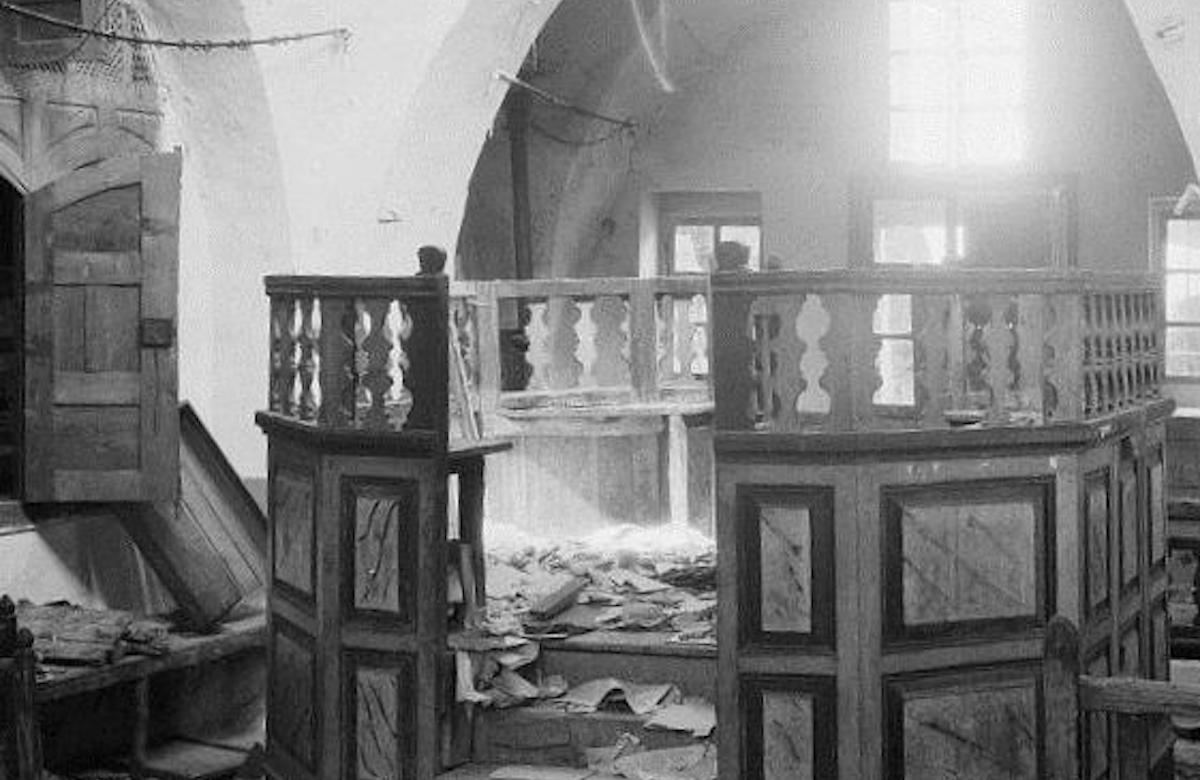

Desecrated Synagogue Hebron - On August 23-24,1929, more than 60 Jewish individuals lost their lives in a tragic incident referred to as the Hebron Massacre. This dark episode later remembered as one of the deadliest attacks on Jewish civilians during the British Rule of Mandatory Palestine.
In 1929, violent clashes erupted, notably the Hebron massacre, where 67 Jews were killed in Palestinian riots against Jewish immigration in Palestine. These events marked early signs of the escalating Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
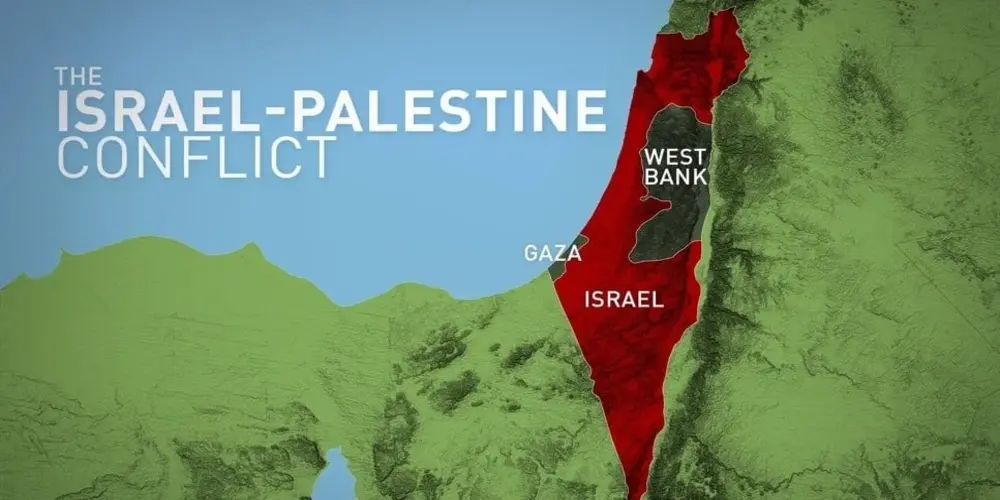
Territories in Dispute
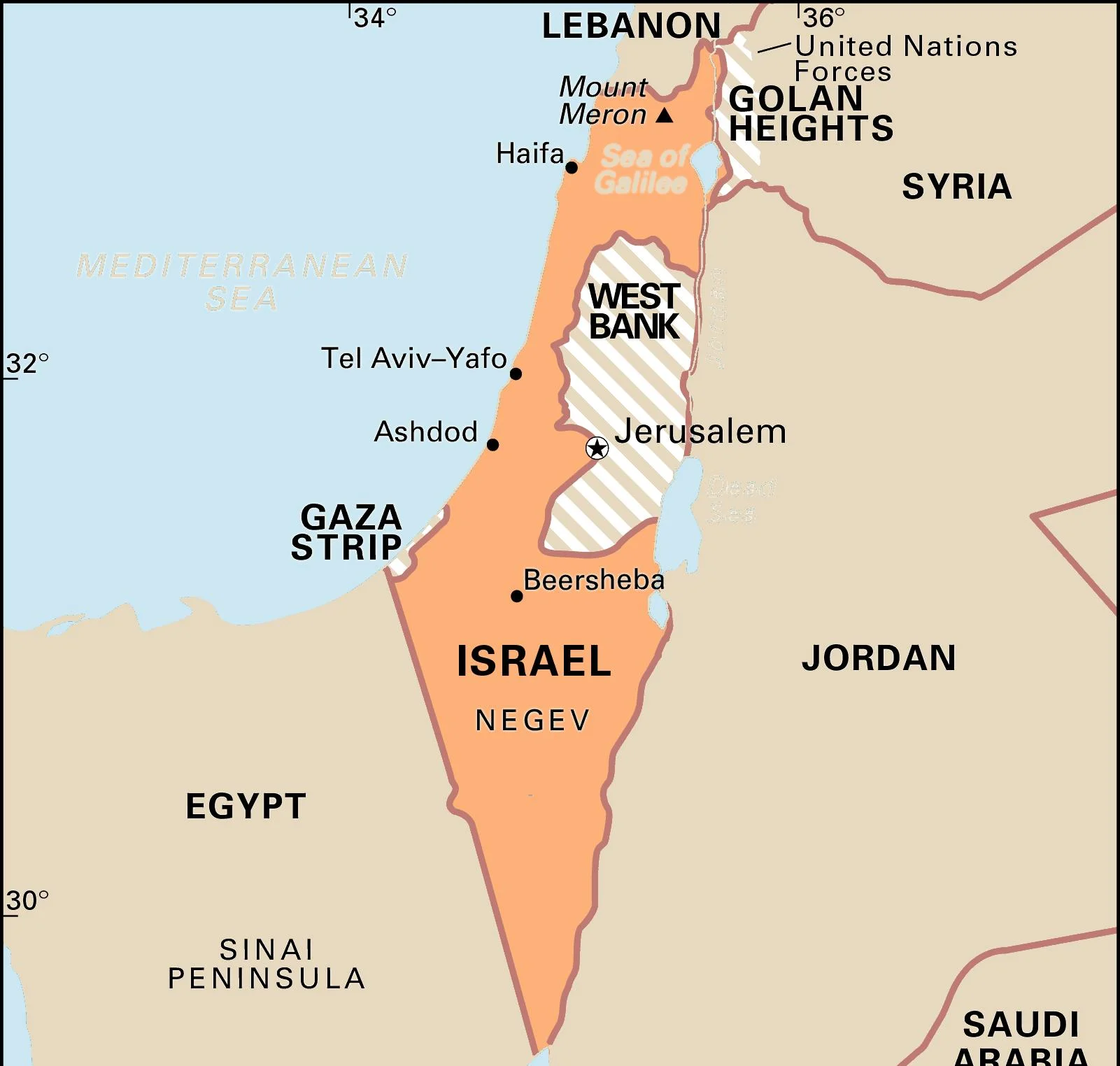
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict encompasses several territories:
- Gaza: Also known as the Gaza Strip, it is home to approximately 2 million Palestinians, many of whom were displaced during the War of Independence.
- West Bank: Located east of Israel, it houses about 3 million Palestinians, predominantly Muslim Arabs. The West Bank holds several Jewish holy sites visited by pilgrims annually.
- East Jerusalem: Jerusalem itself is a divided and disputed city. Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli war, Israel controlled the western portion, while Jordan governed the east. Israel captured the entire city in the 1967 Six-Day War. Although Israel claims Jerusalem as its undivided capital, most nations do not recognize this claim.
Hamas: The Leading Palestinian Terrorist Group
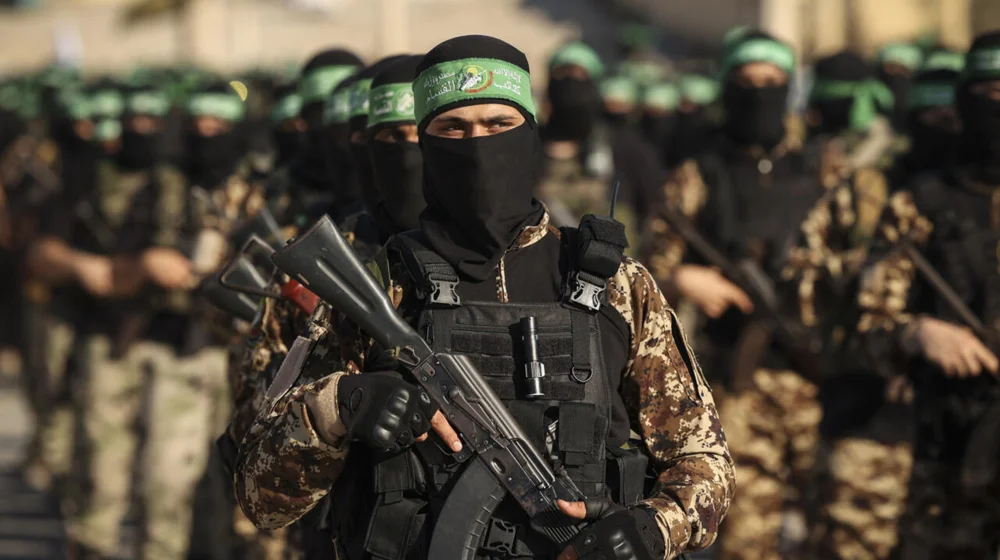

Hamas, founded in 1987 during the first Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupation, is the largest Palestinian terrorist group. It has fired rockets into Israeli cities during the current fighting and has controlled Gaza since its electoral victory 2007. Hamas is dedicated to eliminating Israel and is officially classified as a terrorist organization by numerous nations, including the U.S. and the U.K.
Israeli Defense Forces: Israel’s Armed Might
The Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) comprise the combined armed forces of Israel, including the army, navy, and air force. Established in 1948, two weeks after Israel declared itself a state, the IDF plays a central role in Israel’s defense.
International Efforts for Peace: A Series of Failures
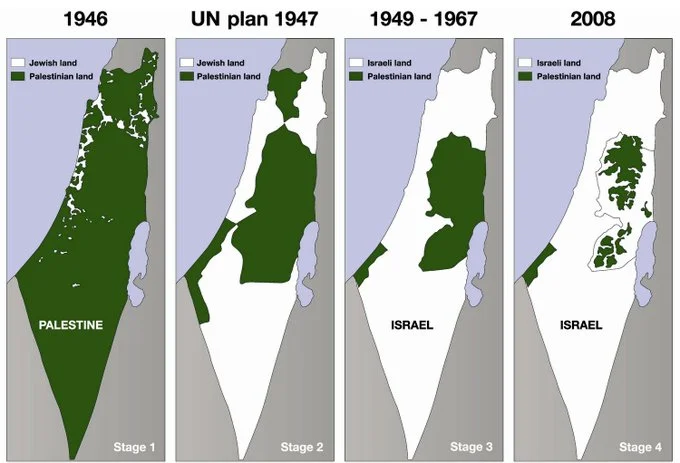
Impact of Israeli-Palestinian Conflict from 1946 to 2008
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has witnessed numerous international attempts at peace, but many have faltered:
- 1947: The United Nations voted to partition Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, designating Jerusalem as an international city. Arab rejection led to the plan’s abandonment.
- 1948: Following the British Mandate’s expiration on May 14, Israel declared itself a state, with U.S. recognition shortly after that and, later, USSR acknowledgment.
- 1949: The Armistice Agreements aimed to mediate peace in Palestine. While Israel signed agreements with Egypt, Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon, formal peace treaties were never realized.
- 1956: Egypt’s nationalization of the Suez Canal led to a conflict involving Israel, Britain, France, and the Soviet Union’s threat of nuclear retaliation, leading to withdrawal.
- 1964: The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) was formed to unite Arab groups and liberate Palestinian territories.
- 1967: The Six-Day War emerged from the Suez Canal crisis, leading to Israel’s capture of territories, including Gaza, West Bank, East Jerusalem, Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula.
- 1973: The Yom Kippur War began on the holiest day of the Jewish year, leading to U.S.-mediated disengagement agreements.
- 1979 Camp David Accords – A Historic Peace Deal: In 1979, the Camp David Accords, brokered by President Jimmy Carter, resulted in a peace deal between Israel and Egypt, leading to Israel’s gradual withdrawal from the Sinai Peninsula.
- 1991 Intifadas and Ongoing Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict saw two intifadas (uprisings) by Palestinians in Gaza, Israel, and the West Bank, marked by boycotts, civil disobedience, and attacks. The first intifada lasted over five years, with significant casualties on both sides. Despite international criticism of Israel’s use of force, tensions persisted.
- 1993 The Oslo I Accord: In 1993, the Oslo I agreement, known as the Declaration of Principles, was signed between Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat. It set a timetable for a Middle East peace process.
- 1995 The Oslo II Accord: In 1995, Oslo II, a second agreement, recognized the state of Israel and allowed limited Palestinian self-government in Gaza.
- 2000 Failed Peace Efforts – Camp David and Second Intifada: In 2000, the Camp David summit aimed to end hostilities but concluded without an agreement. Frustrated Palestinians initiated the second intifada, lasting until 2005 and resulting in substantial casualties.
- 2005 Gaza Withdrawal and Hamas’ Rise: In 2005, Israel withdrew from Gaza while retaining control.
- 2007: In 2007, Hamas won elections in Gaza.
- 2008: In 2008, Israel launched a military campaign against Hamas, resulting in casualties and a ceasefire.
- 2012: Israel targeted Hamas leaders.
- 2014: The Gaza War resulted in casualties and accusations of war crimes.
- 2017: The U.S. recognized Jerusalem as Israel’s capital.
- 2018: Protests erupted on the Gaza-Israeli border.
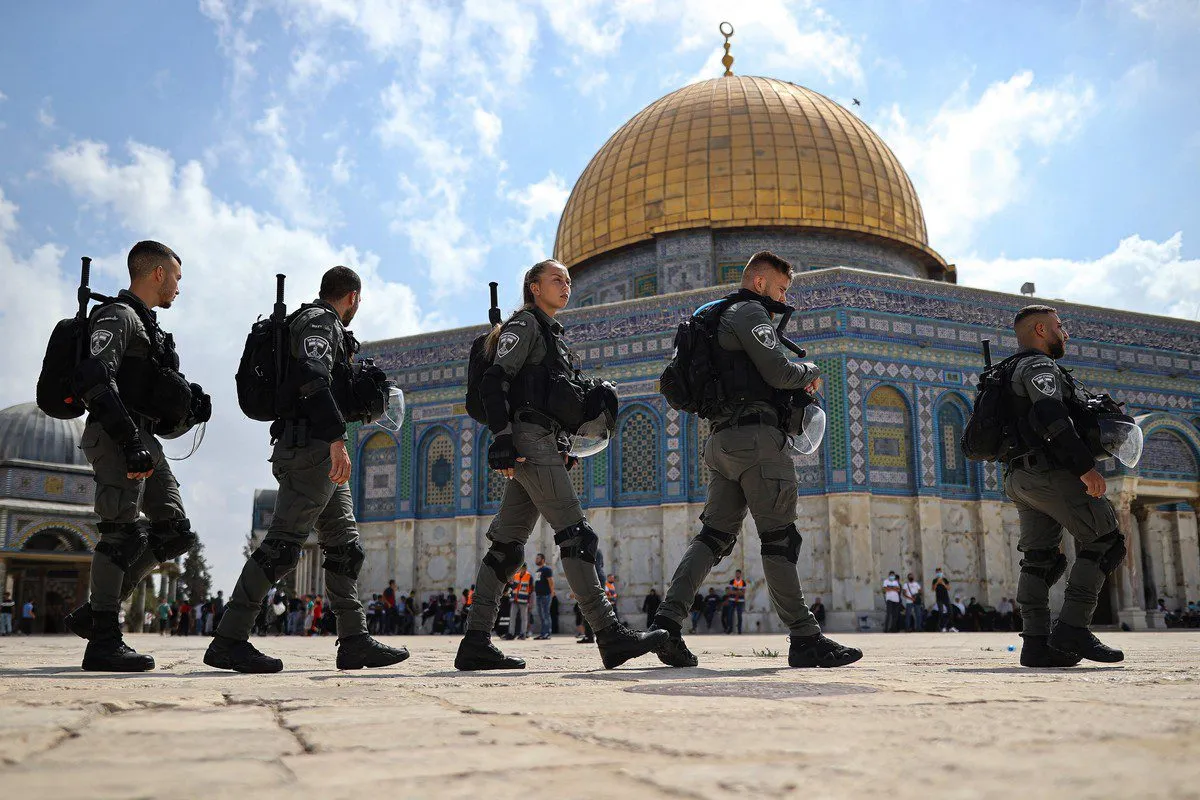

Israeli forces seen in front of the Dome of the Rock, within the Al Aqsa Mosque Compound in Jerusalem on September 10, 2021
- 2021 Recent Tensions and Escalations: Tensions flared in 2021 when Israeli police raided the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem, sparking violence. Rocket attacks and airstrikes followed, culminating in a ceasefire.
- 2022 Preemptive Strikes and Violence: In 2022, Israel responded to a string of terrorist attacks with airstrikes against Iran-backed terrorist groups. A surge in violence resulted in casualties.
- 2023 A Year of Escalation: In January and July 2023, Israel conducted raids in the West Bank, escalating tensions. In October, a massive offensive unfolded as Hamas gunmen infiltrated southern Israel, launching thousands of rockets. This marked one of the most significant Israeli-Palestinian conflict and escalations in years, resulting in numerous casualties.
Continuing Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: Seeking a Path to Peace
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains deeply rooted in history, making finding lasting peace challenging. This timeline provides a comprehensive overview of critical events, tensions, and efforts to resolve the conflict, shedding light on the complexity of this enduring struggle.